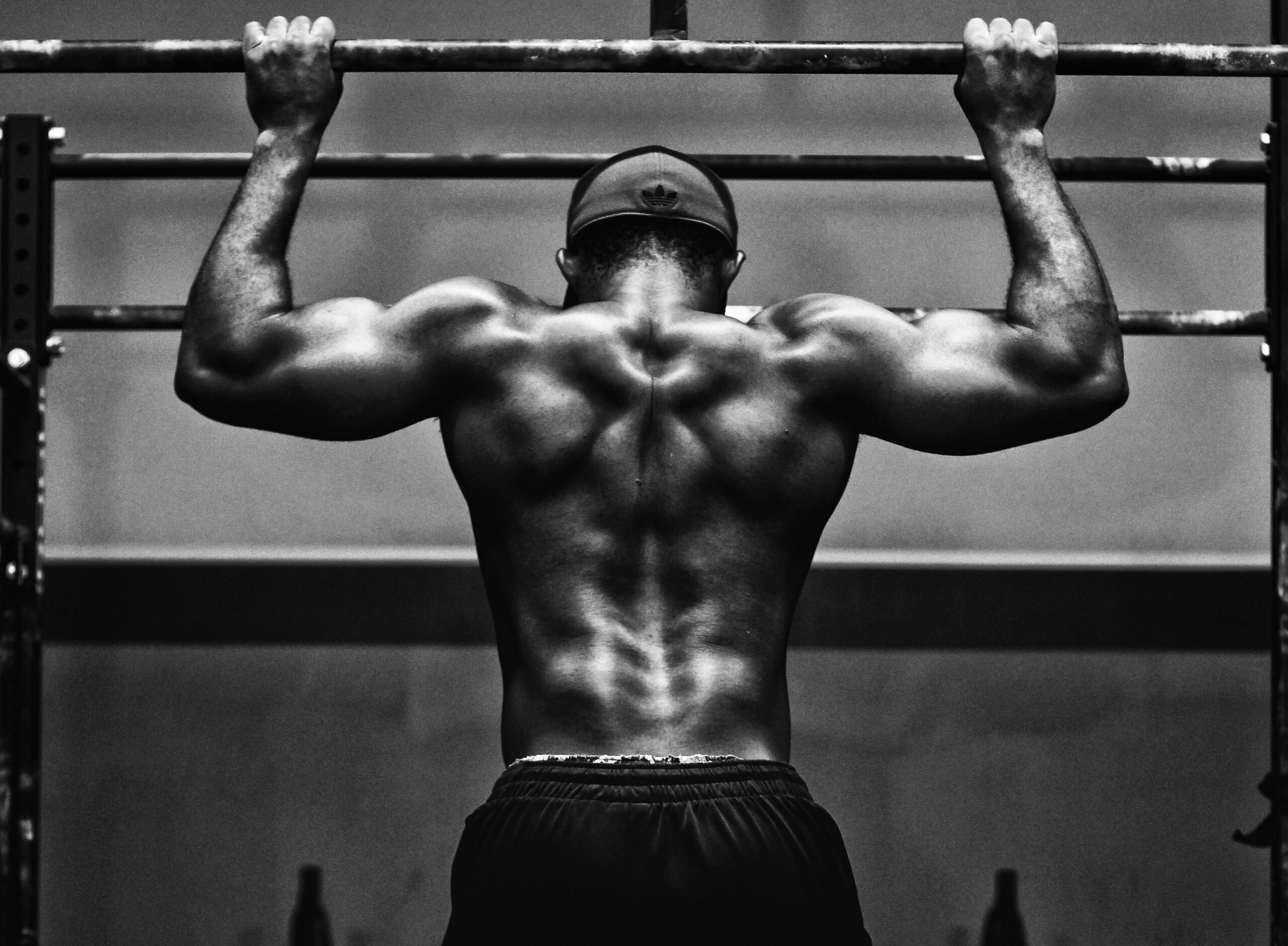
When it comes to physical improvement, building muscle is often the top priority.
Gaining muscle mass will enhance your muscle definition, improve your lean body mass, and add size in all the right places.
Building muscle requires time, persistence, and a long-term commitment to the process. While gaining a significant amount of muscle might seem challenging, with proper training programs and adequate consumption of certain foods, serious muscle building is possible for most people.
This article breaks down everything you need to know about building muscle, including how to work out, what to eat, and recovery protocols.
Basics of Muscle Building
Physically, skeletal muscles are a series of parallel cylindrical fibers that contract to generate force. This muscle contraction allows all external human movements to occur.
Your body is in a continuous process of renewing and recycling amino acids, or the building blocks of proteins, in your muscles.
If your body removes more protein than it adds, you will lose muscle. If net protein synthesis is even, there will be no measurable change in muscle size. Finally, if your body deposits more protein than it removes, your muscles will grow.
The key to building muscle is increasing the rate of protein deposition while decreasing the rate of protein breakdown.
This process of increasing your muscle mass is known as muscle hypertrophy, and it is the primary goal of resistance training.
The muscle-building process is driven by several factors, including hormones like testosterone and growth hormone, as well as the availability of amino acids and other nutrients.
To build new muscle tissue, your primary tools are resistance training to stimulate your body’s rate of protein synthesis and consuming adequate amounts of protein and overall nutrients.
The right amount of resistance training triggers a hormonal response in your body conducive to muscle building, but it requires sufficient protein and energy availability to ensure the process results in muscle gain rather than muscle loss.
While researchers and experts continue to study the science of optimizing muscle gain, resistance training with moderate to heavy weights combined with relatively high protein intake is the only proven method to increase muscle mass.
Tips to Gain Muscle
While various types of exercise offer health benefits, the only way to reliably drive muscle growth is by using your muscles against moderate to heavy resistance. Additionally, muscle growth is specific to the muscles being used.
1. Choose the Right Amount of Weight
In all cases, the weight should be heavy enough that performing more than 20 reps is impossible.
The weight you use should leave you near failure or at failure by the specified number of repetitions.
For instance, if you are doing a set of 10 reps, by the tenth rep, you should be unable or almost unable to perform another rep. If your goal is muscle building, you should rarely have more than “two reps left in the tank” at the end of a set.
The overall implication of the repetition range continuum is that you should go through different phases of training using various rep ranges to see what yields the most muscle growth for your body.
2. Choose Your Exercises Wisely
As mentioned, muscle building is specific to the muscle being worked.
For example, to build bigger biceps, you need to perform exercises that target the biceps. This could be an isolated biceps exercise, such as bicep curls, or a compound movement that involves the biceps, such as pull-ups.
In terms of the best exercise types for muscle building, both compound and isolation movements can be equally effective in producing muscle hypertrophy.
However, for the best long-term fitness results, you should incorporate both compound and isolation movements into your training.
Compound movements like a barbell back squat effectively stimulate multiple large muscle groups in a single exercise and provide more functional movement for real-life activities. This leads to both more efficient workouts and more practical muscle strength.
Isolation movements are a great way to target specific muscles, and beginners may initially find them safer and easier to learn compared to compound movements.
Additionally, it can be easier to perform isolation movements when you are fatigued, as you are not stabilizing your whole body. This can allow you to get some extra targeted sets at the end of your workout when you would otherwise be too tired to perform another compound exercise.
3. Structure Your Workouts to Avoid Overtraining
A good rule of thumb is to perform 3 sets of 3-5 compound movements followed by 3 sets of 1-2 isolation movements per workout.
Typically, you perform your heaviest sets using compound movements and higher rep ranges on your isolation movements. Assuming you perform three working sets per exercise, limit your total combined compound and isolation exercises to 5-7 movements per workout.
This allows you to benefit from each type of exercise while maximizing your training program’s overall muscle-building potential and avoiding any symptoms of overtraining.
How to Eat to Gain Muscle
To gain muscle, you need to provide your body with the right amount of calories and nutrients, especially protein. Doing so will help build new muscle proteins from the dietary protein you consume, inspired by the work you do in the weight room.
Your body has a maximum rate of muscle-building, and beyond that limit, extra calories will be stored as fat. If your goal is to define muscle, you want to avoid gaining too much body fat.
Calories Needed to Gain Muscle:
For sustainable muscle gain without excessive fat, aim to eat 300-500 calories above your baseline needs per day.
Protein Needed to Gain Muscle:
When it comes to nutrients for building muscle, protein is the highest priority. Recent research suggests that those training to gain muscle should eat about 0.72 grams of protein per pound (1.6 grams per kilogram) of body weight per day.
In Summary
Gaining muscle is possible using all repetition ranges, and some people may respond better to either heavy or light weights with low or high repetitions, respectively.
Gaining muscle requires sufficient protein and calories in your diet to fuel growth. Avoid eating more than 300-500 extra calories per day to minimize fat gain.
Gaining muscle takes time and is typically limited to 0.5-2 pounds (0.25-0.9 kg) per month.